Regular expressions are used for Pattern Matching.
Maybe one of the best answers I’ve seen in StackOverflow is this about Regular expressions, from user Portland Runner, but the topic can get as tricky as this answer show, epic!.
Following are a series of procedures to perform Regular Expressions operations. You can work with “Early binding” (set a reference to Microsoft VBScript Regular Expressions 5.5) or with “Late binding” through objects.
Anchoring Patterns:
Precedence table:
Predefined Character Abbreviations:
Example 1: Run as macro The following example macro looks at the value in cell
Example 2: Run as an in-cell function This example is the same as example 1 but is setup to run as an in-cell function. To use, change the code to this: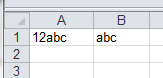
Example 3: Loop Through Range This example is the same as example 1 but loops through a range of cells.
Example 4: Splitting apart different patterns This example loops through a range (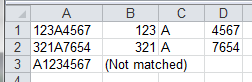
Additional Pattern Examples
Finally, there is this version of an UDF to use Regular Expressions, on the same post answer as the one above:
Early binding
- Press ALT+F11 to access to the VBE.
- Select “Tools” from the top menu.
- Select “References”, and check the box of “Microsoft VBScript Regular Expressions 5.5” to include in your workbook.
- Click “OK”
Patterns
Basic definitions:- Range.
- E.g.
a-zmatches an lower case letters from a to z - E.g.
0-5matches any number from 0 to 5
[] Match exactly one of the objects inside these brackets.
- E.g.
[a]matches the letter a - E.g.
[abc]matches a single letter which can be a, b or c - E.g.
[a-z]matches any single lower case letter of the alphabet.
() Groups different matches for return purposes. See examples below.
{} Multiplier for repeated copies of pattern defined before it.
- E.g.
[a]{2}matches two consecutive lower case letter a:aa - E.g.
[a]{1,3}matches at least one and up to three lower case lettera,aa,aaa
+ Match at least one, or more, of the pattern defined before it.
- E.g.
a+will match consecutive a’sa,aa,aaa, and so on
? Match zero or one of the pattern defined before it.
- E.g. Pattern may or may not be present but can only be matched one time.
- E.g.
[a-z]?matches empty string or any single lower case letter.
* Match zero or more of the pattern defined before it.
– E.g. Wildcard for pattern that may or may not be present.
– E.g. [a-z]* matches empty string or string of lower case letters.
. Matches any character except newline \n
- E.g.
a.Matches a two character string starting with a and ending with anything except\n
| OR operator
- E.g.
a|bmeans eitheraorbcan be matched. - E.g.
red|white|orangematches exactly one of the colors.
^ NOT operator
- E.g.
[^0-9]character can not contain a number - E.g.
[^aA]character can not be lower caseaor upper caseA
\ Escapes special character that follows (overrides above behavior)
- E.g.
\.,\\,\(,\?,\$,\^
Anchoring Patterns:
^ Match must occur at start of string
- E.g.
^aFirst character must be lower case lettera - E.g.
^[0-9]First character must be a number.
$ Match must occur at end of string
- E.g.
a$Last character must be lower case lettera
Precedence table:
Order Name Representation
1 Parentheses ( )
2 Multipliers ? + * {m,n} {m, n}?
3 Sequence & Anchors abc ^ $
4 Alternation |Predefined Character Abbreviations:
abr same as meaning
\d [0-9] Any single digit
\D [^0-9] Any single character that's not a digit
\w [a-zA-Z0-9_] Any word character
\W [^a-zA-Z0-9_] Any non-word character
\s [ \r\t\n\f] Any space character
\S [^ \r\t\n\f] Any non-space character
\n [\n] New lineExample 1: Run as macro The following example macro looks at the value in cell
A1 to see if the first 1 or 2 characters are digits. If so, they are removed and the rest of the string is displayed. If not, then a box appears telling you that no match is found. Cell A1 values of 12abc will return abc, value of 1abc will return abc, value of abc123 will return “Not Matched” because the digits were not at the start of the string.
Private Sub simpleRegex()
Dim strPattern As String: strPattern = "^[0-9]{1,2}"
Dim strReplace As String: strReplace = ""
'Dim regEx As New RegExp
Dim regEx As Object: Set regEx = CreateObject("VBScript.RegExp")
Dim strInput As String
Dim Myrange As Excel.Range
Set Myrange = ActiveSheet.Range("A1")
If strPattern "" Then
strInput = Myrange.Value
With regEx
.Global = True
.MultiLine = True
.IgnoreCase = False
.Pattern = strPattern
End With
If regEx.Test(strInput) Then
MsgBox (regEx.Replace(strInput, strReplace))
Else
MsgBox ("Not matched")
End If
End If
Set regEx = Nothing
End SubExample 2: Run as an in-cell function This example is the same as example 1 but is setup to run as an in-cell function. To use, change the code to this:
Function simpleCellRegex(Myrange As Excel.Range) As String
'Dim regEx As New RegExp
Dim regEx As Object: Set regEx = CreateObject("VBScript.RegExp")
Dim strPattern As String
Dim strInput As String
Dim strReplace As String
Dim strOutput As String
strPattern = "^[0-9]{1,3}"
If strPattern "" Then
strInput = Myrange.Value
strReplace = ""
With regEx
.Global = True
.MultiLine = True
.IgnoreCase = False
.Pattern = strPattern
End With
If regEx.test(strInput) Then
simpleCellRegex = regEx.Replace(strInput, strReplace)
Else
simpleCellRegex = "Not matched"
End If
End If
Set regEx = Nothing
End FunctionA1. Enter this formula =simpleCellRegex(A1) in cell B1 and the result will be “abc”.

Example 3: Loop Through Range This example is the same as example 1 but loops through a range of cells.
Private Sub simpleRegex()
Dim strPattern As String: strPattern = "^[0-9]{1,2}"
Dim strReplace As String: strReplace = ""
'Dim regEx As New RegExp
Dim regEx As Object: Set regEx = CreateObject("VBScript.RegExp")
Dim strInput As String
Dim Myrange As Excel.Range
Set Myrange = ActiveSheet.Range("A1:A5")
For Each cell In Myrange
If strPattern "" Then
strInput = cell.Value
With regEx
.Global = True
.MultiLine = True
.IgnoreCase = False
.Pattern = strPattern
End With
If regEx.Test(strInput) Then
MsgBox (regEx.Replace(strInput, strReplace))
Else
MsgBox ("Not matched")
End If
End If
Next
Set regEx = Nothing
End SubExample 4: Splitting apart different patterns This example loops through a range (
A1, A2 & A3) and looks for a string starting with three digits followed by a single alpha character and then 4 numeric digits. The output splits apart the pattern matches into adjacent cells by using the (). $1 represents the first pattern matched within the first set of ().
Private Sub splitUpRegexPattern()
'Dim regEx As New RegExp
Dim regEx As Object: Set regEx = CreateObject("VBScript.RegExp")
Dim strPattern As String
Dim strInput As String
Dim Myrange As Excel.Range
Set Myrange = ActiveSheet.Range("A1:A3")
For Each C In Myrange
strPattern = "(^[0-9]{3})([a-zA-Z])([0-9]{4})"
If strPattern "" Then
strInput = C.Value
With regEx
.Global = True
.MultiLine = True
.IgnoreCase = False
.Pattern = strPattern
End With
If regEx.test(strInput) Then
C.Offset(0, 1) = regEx.Replace(strInput, "$1")
C.Offset(0, 2) = regEx.Replace(strInput, "$2")
C.Offset(0, 3) = regEx.Replace(strInput, "$3")
Else
C.Offset(0, 1) = "(Not matched)"
End If
End If
Next
Set regEx = Nothing
End Sub
Additional Pattern Examples
String Regex Pattern Explanation
a1aaa [a-zA-Z][0-9][a-zA-Z]{3} Single alpha, single digit, three alpha characters
a1aaa [a-zA-Z]?[0-9][a-zA-Z]{3} May or may not have preceeding alpha character
a1aaa [a-zA-Z][0-9][a-zA-Z]{0,3} Single alpha, single digit, 0 to 3 alpha characters
a1aaa [a-zA-Z][0-9][a-zA-Z]* Single alpha, single digit, followed by any number of alpha characters
</i8> \<\/[a-zA-Z][0-9]\> Exact non-word character except any single alpha followed by any single digit
Function regex(strInput As String, matchPattern As String, Optional ByVal outputPattern As String = "$0") As Variant
Dim inputRegexObj As New VBScript_RegExp_55.RegExp, outputRegexObj As New VBScript_RegExp_55.RegExp, outReplaceRegexObj As New VBScript_RegExp_55.RegExp
Dim inputMatches As Object, replaceMatches As Object, replaceMatch As Object
Dim replaceNumber As Integer
With inputRegexObj
.Global = True
.MultiLine = True
.IgnoreCase = False
.Pattern = matchPattern
End With
With outputRegexObj
.Global = True
.MultiLine = True
.IgnoreCase = False
.Pattern = "\$(\d+)"
End With
With outReplaceRegexObj
.Global = True
.MultiLine = True
.IgnoreCase = False
End With
Set inputMatches = inputRegexObj.Execute(strInput)
If inputMatches.Count = 0 Then
regex = False
Else
Set replaceMatches = outputRegexObj.Execute(outputPattern)
For Each replaceMatch In replaceMatches
replaceNumber = replaceMatch.SubMatches(0)
outReplaceRegexObj.Pattern = "\$" & replaceNumber
If replaceNumber = 0 Then
outputPattern = outReplaceRegexObj.Replace(outputPattern, inputMatches(0).Value)
Else
If replaceNumber > inputMatches(0).SubMatches.Count Then
'regex = "A to high $ tag found. Largest allowed is $" & inputMatches(0).SubMatches.Count & "."
regex = CVErr(xlErrValue)
Exit Function
Else
outputPattern = outReplaceRegexObj.Replace(outputPattern, inputMatches(0).SubMatches(replaceNumber - 1))
End If
End If
Next
regex = outputPattern
End If
End Function
[/sourcecode]